【枚举】重排字符形成目标字符串
题目
给你两个下标从 0 开始的字符串 s 和 target 。你可以从 s 取出一些字符并将其重排,得到若干新的字符串。
从 s 中取出字符并重新排列,返回可以形成 target 的 最大 副本数。
示例 1:
| |
示例 2:
| |
示例 3:
| |
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 1001 <= target.length <= 10s和target由小写英文字母组成
解题思路
枚举。
代码
| |
【模拟】价格减免
题目
句子 是由若干个单词组成的字符串,单词之间用单个空格分隔,其中每个单词可以包含数字、小写字母、和美元符号 '$' 。如果单词的形式为美元符号后跟着一个非负实数,那么这个单词就表示一个价格。
- 例如
"$100"、"$23"和"$6.75"表示价格,而"100"、"$"和"2$3"不是。
**注意:**本题输入中的价格均为整数。
给你一个字符串 sentence 和一个整数 discount 。对于每个表示价格的单词,都在价格的基础上减免 discount% ,并 更新 该单词到句子中。所有更新后的价格应该表示为一个 恰好保留小数点后两位 的数字。
返回表示修改后句子的字符串。
示例 1:
| |
示例 2:
| |
提示:
1 <= sentence.length <= 10^5sentence由小写英文字母、数字、' '和'$'组成sentence不含前导和尾随空格sentence的所有单词都用单个空格分隔- 所有价格都是 正 整数且不含前导零
- 所有价格 最多 为
10位数字 0 <= discount <= 100
解题思路
C++做这题真的人麻了。
两个坑吧,一个是价格最多为10位数字,用stoi函数将string转int时是不够的,可能会溢出,要用stol函数;
一个是精度问题。利用字符串流。
| |
代码
| |
偷学代码
用python很舒服
| |
【单调栈+DP】使数组按非递减顺序排列
题目
给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数数组 nums 。在一步操作中,移除所有满足 nums[i - 1] > nums[i] 的 nums[i] ,其中 0 < i < nums.length 。
重复执行步骤,直到 nums 变为 非递减 数组,返回所需执行的操作数。
示例 1:
| |
示例 2:
| |
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 10^51 <= nums[i] <= 10^9
解题思路
元素 x 会被左边某个比他大的元素 y 给删除(如果存在的话)。
我们需要计算在删除 x 之前,删除了多少个比 y 小的元素,从而算出删除 x 的时刻(第几步操作)。
答案可以转换成所有元素被删除的时刻的最大值。
考虑每一个数被删除的时间点。如果num[i]左侧没有比它更大的数,那么该数不会被删除;如果左侧有比它更大的数,记左侧最近比它大的数的位置为L,那么num[L+1..i]这几个数都可以看成是被num[L]删除的,此时t[i]=max(t[L+1..i-1])+1,即在中间的数删除后加1。
单调栈+DP+线段树
| |
单调栈+DP
仅仅使用单调栈也是可以的。
| |
【最短路】到达角落需要移除障碍物的最小数目
题目
给你一个下标从 0 开始的二维整数数组 grid ,数组大小为 m x n 。每个单元格都是两个值之一:
0表示一个 空 单元格,1表示一个可以移除的 障碍物 。
你可以向上、下、左、右移动,从一个空单元格移动到另一个空单元格。
现在你需要从左上角 (0, 0) 移动到右下角 (m - 1, n - 1) ,返回需要移除的障碍物的 最小 数目。
示例 1:
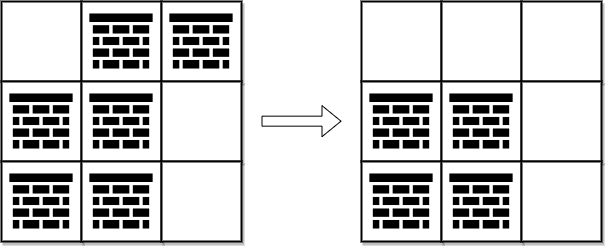
| |
示例 2:
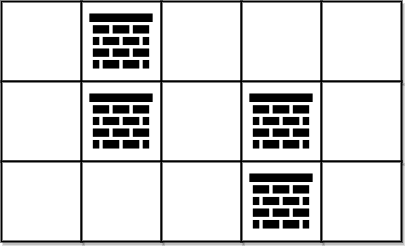
| |
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 10^52 <= m * n <= 10^5grid[i][j]为0或1grid[0][0] == grid[m - 1][n - 1] == 0
解题思路
一开始没想到用最短路相关算法做。
只想着用BFS+优先队列,一路标记状态避免访问重复状态,最先到达终点时就是最小移除障碍数目。标记状态时,状态有3部分。
这种做法很接近堆优化的Dijkstra算法了。
注意一点,优先队列priority_queue默认是最大堆,要么在结构体定义<号时反过来,要么还是在结构体中正常定义,但是将堆声明为最小堆(这种方式好像不行,只能在结构体定义中注意一下了)。
代码1.0(TLE)
状态是3元组,用set存自定义结构体。超时了。
| |
代码2.0(TLE)
将set换成unordered_set,需要自定义哈希方法,结果需要的时间反而更多?通过样例更少
| |
代码3.0(堆优化的Dijkstra)
将空白处的2个节点相互之间是一条权值为0的边,与障碍物则是一条权值为1的边,实际上这题就是最短路径问题。
dst[x,y] 起点到该点的最短距离
| |
代码4.0(01BFS)
BFS为什么能求最短路径。在每个权值相同的情况下,BFS求的是最短路径。像这种只有0和另一权值的,也可以用BFS,不过一个队列是不够的,要么拿两个队列,要么拿一个双端队列,0的话加在开头,另一权值的加在末尾。
即不用到优先队列,就可以判断最短距离。注意,只有权值为0和其他值才可以,但是如果是2个不为0的,就不能保证。
| |
