
【模拟】计算应缴税款总额
题目
给你一个下标从 0 开始的二维整数数组 brackets ,其中 brackets[i] = [upperi, percenti] ,表示第 i 个税级的上限是 upperi ,征收的税率为 percenti 。税级按上限 从低到高排序(在满足 0 < i < brackets.length 的前提下,upperi-1 < upperi)。
税款计算方式如下:
- 不超过
upper0 的收入按税率 percent0 缴纳 - 接着
upper1 - upper0 的部分按税率 percent1 缴纳 - 然后
upper2 - upper1 的部分按税率 percent2 缴纳 - 以此类推
给你一个整数 income 表示你的总收入。返回你需要缴纳的税款总额。与标准答案误差不超 10-5 的结果将被视作正确答案。
示例 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| 输入:brackets = [[3,50],[7,10],[12,25]], income = 10
输出:2.65000
解释:
前 $3 的税率为 50% 。需要支付税款 $3 * 50% = $1.50 。
接下来 $7 - $3 = $4 的税率为 10% 。需要支付税款 $4 * 10% = $0.40 。
最后 $10 - $7 = $3 的税率为 25% 。需要支付税款 $3 * 25% = $0.75 。
需要支付的税款总计 $1.50 + $0.40 + $0.75 = $2.65 。
|
示例 2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| 输入:brackets = [[1,0],[4,25],[5,50]], income = 2
输出:0.25000
解释:
前 $1 的税率为 0% 。需要支付税款 $1 * 0% = $0 。
剩下 $1 的税率为 25% 。需要支付税款 $1 * 25% = $0.25 。
需要支付的税款总计 $0 + $0.25 = $0.25 。
|
示例 3:
1
2
3
4
| 输入:brackets = [[2,50]], income = 0
输出:0.00000
解释:
没有收入,无需纳税,需要支付的税款总计 $0 。
|
提示:
1 <= brackets.length <= 1001 <= upperi <= 10000 <= percenti <= 1000 <= income <= 1000upperi 按递增顺序排列upperi 中的所有值 互不相同- 最后一个税级的上限大于等于
income
解题思路
简单模拟。
WA了一发,在income<=b[0][0]时就可以直接返回了,否则的话后面要判断rst是否大于0
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| class Solution {
public:
double calculateTax(vector<vector<int>>& brackets, int income) {
int n = brackets.size();
double res = 0.0;
if(income<=brackets[0][0]) res = 1.00*income*brackets[0][1]/100;
else res = brackets[0][0]*1.00*brackets[0][1]/100;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
if(income>=brackets[i][0]){
int rst = brackets[i][0]-brackets[i-1][0];
res += 1.00*rst*brackets[i][1]/100;
}else{
int rst = income-brackets[i-1][0];
if(rst>0) res += 1.00*rst*brackets[i][1]/100;
break;
}
}
return res;
}
};
|
【动态规划】网格中的最小路径代价
题目
给你一个下标从 0 开始的整数矩阵 grid ,矩阵大小为 m x n ,由从 0 到 m * n - 1 的不同整数组成。你可以在此矩阵中,从一个单元格移动到 下一行 的任何其他单元格。如果你位于单元格 (x, y) ,且满足 x < m - 1 ,你可以移动到 (x + 1, 0), (x + 1, 1), …, (x + 1, n - 1) 中的任何一个单元格。注意: 在最后一行中的单元格不能触发移动。
每次可能的移动都需要付出对应的代价,代价用一个下标从 0 开始的二维数组 moveCost 表示,该数组大小为 (m * n) x n ,其中 moveCost[i][j] 是从值为 i 的单元格移动到下一行第 j 列单元格的代价。从 grid 最后一行的单元格移动的代价可以忽略。
grid 一条路径的代价是:所有路径经过的单元格的 值之和 加上 所有移动的 代价之和 。从 第一行 任意单元格出发,返回到达 最后一行 任意单元格的最小路径代价*。*
示例 1:
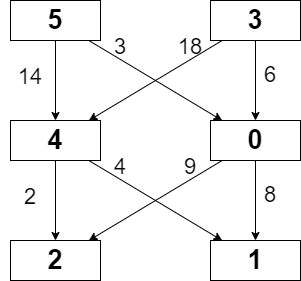
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| 输入:grid = [[5,3],[4,0],[2,1]], moveCost = [[9,8],[1,5],[10,12],[18,6],[2,4],[14,3]]
输出:17
解释:最小代价的路径是 5 -> 0 -> 1 。
- 路径途经单元格值之和 5 + 0 + 1 = 6 。
- 从 5 移动到 0 的代价为 3 。
- 从 0 移动到 1 的代价为 8 。
路径总代价为 6 + 3 + 8 = 17 。
|
示例 2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| 输入:grid = [[5,1,2],[4,0,3]], moveCost = [[12,10,15],[20,23,8],[21,7,1],[8,1,13],[9,10,25],[5,3,2]]
输出:6
解释:
最小代价的路径是 2 -> 3 。
- 路径途经单元格值之和 2 + 3 = 5 。
- 从 2 移动到 3 的代价为 1 。
路径总代价为 5 + 1 = 6 。
|
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length2 <= m, n <= 50grid 由从 0 到 m * n - 1 的不同整数组成moveCost.length == m * nmoveCost[i].length == n1 <= moveCost[i][j] <= 100
解题思路
简单路径规划类DP
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
class Solution {
public:
int minPathCost(vector<vector<int>>& grid, vector<vector<int>>& moveCost) {
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
int res = INF;
vector<vector<int>> dp(n,vector<int>(m,INF));
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
dp[0][j] = grid[0][j];
}
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
for(int k=0;k<m;k++){
dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][j], grid[i][j]+dp[i-1][k]+moveCost[grid[i-1][k]][j]);
}
}
}
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
res = min(res,dp[n-1][j]);
}
return res;
}
};
|
【DFS/状压DP】公平分发饼干
题目
给你一个整数数组 cookies ,其中 cookies[i] 表示在第 i 个零食包中的饼干数量。另给你一个整数 k 表示等待分发零食包的孩子数量,所有 零食包都需要分发。在同一个零食包中的所有饼干都必须分发给同一个孩子,不能分开。
分发的 不公平程度 定义为单个孩子在分发过程中能够获得饼干的最大总数。
返回所有分发的最小不公平程度。
示例 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| 输入:cookies = [8,15,10,20,8], k = 2
输出:31
解释:一种最优方案是 [8,15,8] 和 [10,20] 。
- 第 1 个孩子分到 [8,15,8] ,总计 8 + 15 + 8 = 31 块饼干。
- 第 2 个孩子分到 [10,20] ,总计 10 + 20 = 30 块饼干。
分发的不公平程度为 max(31,30) = 31 。
可以证明不存在不公平程度小于 31 的分发方案。
|
示例 2:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| 输入:cookies = [6,1,3,2,2,4,1,2], k = 3
输出:7
解释:一种最优方案是 [6,1]、[3,2,2] 和 [4,1,2] 。
- 第 1 个孩子分到 [6,1] ,总计 6 + 1 = 7 块饼干。
- 第 2 个孩子分到 [3,2,2] ,总计 3 + 2 + 2 = 7 块饼干。
- 第 3 个孩子分到 [4,1,2] ,总计 4 + 1 + 2 = 7 块饼干。
分发的不公平程度为 max(7,7,7) = 7 。
可以证明不存在不公平程度小于 7 的分发方案。
|
提示:
2 <= cookies.length <= 81 <= cookies[i] <= 10^52 <= k <= cookies.length
解题思路
看数据规模,n最大值为8,考虑DFS,一遍过了没优化
也想过可以用状压DP,赛时不敢用不熟练的状压DP
代码
DFS 1.0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> num;
vector<int> cook;
int n,res,k;
void dfs(int x){
if(x==n){
int maxv=0;
for(auto &p: num){
maxv = max(maxv,p);
}
res = min(res,maxv);
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
num[i] += cook[x];
dfs(x+1);
num[i] -= cook[x];
}
}
int distributeCookies(vector<int>& cookies, int k) {
n = cookies.size();
cook = cookies;
res = INF;
this->k=k;
num.assign(k,0);
dfs(0);
return res;
}
};
|
DFS 2.0
可以考虑记录当前最大值进行剪枝。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> num;
vector<int> cook;
int n,res,k;
void dfs(int x, int curmax){
if(curmax>=res) return;
if(x==n){
int maxv=0;
for(auto &p: num){
maxv = max(maxv,p);
}
res = min(res,maxv);
return;
}
int tmpmax=curmax;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++){
num[i] += cook[x];
curmax = max(curmax, cook[x]);
dfs(x+1,curmax);
num[i] -= cook[x];
curmax = tmpmax;
}
}
int distributeCookies(vector<int>& cookies, int k) {
n = cookies.size();
cook = cookies;
res = INF;
this->k=k;
num.assign(k,0);
dfs(0,0);
return res;
}
};
|
状压DP
主要是考虑第i个孩子状态为state时,枚举前i-1个孩子的子状态j(state的子集)),补集为state^j
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class Solution {
public:
int distributeCookies(vector<int>& cookies, int k) {
int n = cookies.size();
vector<int> num(1<<n, 0);//num[state] 饼干状态为state时的饼干数量
for(int state=0;state<(1<<n);state++){
int cur=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if((state>>i)&1) cur+=cookies[i];
}
num[state] = cur;
}
vector<vector<int>> dp(n, vector<int>(1<<n, 0));
//dp[i][state] 前i个孩子,选择的饼干状态为state时 单个孩子最大饼干数量的最小值
for(int state=0;state<(1<<n);state++){
dp[0][state] = num[state];
}
for(int i=1;i<k;i++){
for(int state=0;state<(1<<n);state++){
dp[i][state] = INT_MAX;
for(int j=state;j;j=(j-1)&state){//枚举state的子集
dp[i][state]=min(dp[i][state], max(dp[i-1][j],num[state^j]));
}
}
}
return dp[k-1][(1<<n)-1];
}
};
|
状压DP 空间优化
类似于01背包,将第二维逆序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Solution {
public:
int distributeCookies(vector<int>& cookies, int k) {
int n = cookies.size();
vector<int> num(1<<n, 0);//num[state] 饼干状态为state时的饼干数量
for(int state=0;state<(1<<n);state++){
int cur=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if((state>>i)&1) cur+=cookies[i];
}
num[state] = cur;
}
vector<int> dp(1<<n);
//dp[i][state] 前i个孩子,选择的饼干状态为state时 单个孩子最大饼干数量的最小值
dp = num;
for(int i=1;i<k;i++){
for(int state=(1<<n)-1;state>=0;state--){
for(int j=state;j;j=(j-1)&state){//枚举state的子集
dp[state]=min(dp[state], max(dp[j],num[state^j]));
}
}
}
return dp[(1<<n)-1];
}
};
|
【枚举+计数】公司命名
题目
给你一个字符串数组 ideas 表示在公司命名过程中使用的名字列表。公司命名流程如下:
- 从
ideas 中选择 2 个 不同 名字,称为 ideaA 和 ideaB 。 - 交换
ideaA 和 ideaB 的首字母。 - 如果得到的两个新名字 都 不在
ideas 中,那么 ideaA ideaB(串联 ideaA 和 ideaB ,中间用一个空格分隔)是一个有效的公司名字。 - 否则,不是一个有效的名字。
返回 不同 且有效的公司名字的数目。
示例 1:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| 输入:ideas = ["coffee","donuts","time","toffee"]
输出:6
解释:下面列出一些有效的选择方案:
- ("coffee", "donuts"):对应的公司名字是 "doffee conuts" 。
- ("donuts", "coffee"):对应的公司名字是 "conuts doffee" 。
- ("donuts", "time"):对应的公司名字是 "tonuts dime" 。
- ("donuts", "toffee"):对应的公司名字是 "tonuts doffee" 。
- ("time", "donuts"):对应的公司名字是 "dime tonuts" 。
- ("toffee", "donuts"):对应的公司名字是 "doffee tonuts" 。
因此,总共有 6 个不同的公司名字。
下面列出一些无效的选择方案:
- ("coffee", "time"):在原数组中存在交换后形成的名字 "toffee" 。
- ("time", "toffee"):在原数组中存在交换后形成的两个名字。
- ("coffee", "toffee"):在原数组中存在交换后形成的两个名字。
|
示例 2:
1
2
3
| 输入:ideas = ["lack","back"]
输出:0
解释:不存在有效的选择方案。因此,返回 0 。
|
提示:
2 <= ideas.length <= 5 * 10^41 <= ideas[i].length <= 10ideas[i] 由小写英文字母组成ideas 中的所有字符串 互不相同
解题思路
赛时想到了要按首字母分组
同时记录每个组后缀相同情况
但赛时还是紧张了,只想到了记录是否有相同后缀,没有去记录有相同后缀的个数!可惜
代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| class Solution {
public:
long long distinctNames(vector<string>& ideas) {
int n = ideas.size();
vector<unordered_set<string>> tab(26);
for(auto &str: ideas){
int type=str[0]-'a';
string suf(str.begin()+1,str.end());
tab[type].insert(suf);
}
long long res = 0;
int same[26][26];
memset(same,0,sizeof(same));
for(int i=0;i<26;i++){
if(tab[i].empty()) continue;
for(int j=0;j<26;j++){
if(i==j||tab[j].empty()) continue;
same[i][j]=0;//以i开头和以j开头的字符串相同后缀的个数
for(auto &str: tab[i]){
if(tab[j].count(str)){
same[i][j]++;
}
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<26;i++){
if(tab[i].empty()) continue;
for(int j=0;j<26;j++){
if(i==j||tab[j].empty()) continue;
// for(auto &str: tab[i]){
// if(!tab[j].count(str)){
// res += tab[j].size()-same[i][j];
// }
// }
res+=tab[i].size()*tab[j].size()-same[i][j]*tab[j].size()-same[j][i]*tab[i].size()+same[i][j]*same[j][i];//容斥原理
}
}
return res;
}
};
|


